Intro: Are Zero Sugar Drinks Too Good to Be True?
"No sugar. No calories. All the energy."
That’s the promise plastered across almost every energy drink aisle today. From sleek cans labeled "guilt-free" to bright slogans shouting "sugar-free boost," modern beverages have gone all-in on artificial sweeteners. But are we really doing our bodies a favor when we swap real sugar for the lab-made stuff?
A growing body of research is starting to say: maybe not.
In this article, we’ll break down:
-
What artificial sweeteners actually are
-
New studies raising red flags
-
The quiet power of honey as nature's original sweetener
-
Why our clean-label Manuka honey elixir takes a very different path
Let’s dive in.
What Is an Artificial Sweetener, Really?
Artificial sweeteners are synthetic sugar substitutes. They’re often hundreds of times sweeter than real sugar but contain almost no calories.
Common ones you’ll see on ingredient labels:
-
Sucralose (often branded as Splenda)
-
Aspartame (used in Diet Coke)
-
Acesulfame Potassium (Ace-K)
-
Erythritol and Xylitol (sugar alcohols)
-
Stevia (technically plant-derived, but often highly refined)
These are the go-to sweeteners in most "zero sugar" drinks, especially energy drinks.
🚨 New Research Raises Alarms
Recent studies are starting to show a darker side to these sweeteners:
-
A 2023 study linked erythritol (a common sugar alcohol) to increased risk of blood clots and stroke.
-
Sucralose, once considered safe, has been shown to cause gut microbiome disruptions and potential DNA damage in preliminary trials.
-
Some sweeteners like aspartame have long faced scrutiny due to neurological and metabolic concerns.
Even "natural" sweeteners like highly processed stevia extracts are under the microscope for how they interact with insulin and metabolism.
The FDA classifies most of these as GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe). But new independent research is showing that GRAS doesn’t always mean harmless.
❓What Does "Zero Sugar" Really Mean?
Brands love to slap "no sugar" or "zero carbs" on their labels. But here’s what that usually hides:
-
Artificial sweeteners that your body may still react to
-
Unregulated blends of sugar alcohols and fillers
-
Flavorings and chemicals to mask the metallic or artificial aftertaste
Sometimes you’re not drinking less sugar — you’re drinking more confusion.
🍯 Honey: The Sweetener That Stood the Test of Time
Before food labs and artificial formulas, there was honey. And it wasn’t just a sweet treat — it was medicine.
Here’s why honey still holds up:
-
Naturally antimicrobial: Helps preserve and protect
-
Rich in antioxidants: Especially raw and Manuka varieties
-
Supports gut health: Unlike most artificial sweeteners
-
Unprocessed fuel: Real energy your body recognizes
And yes, honey does contain sugars — but they come with nutrients, not just empty calories.
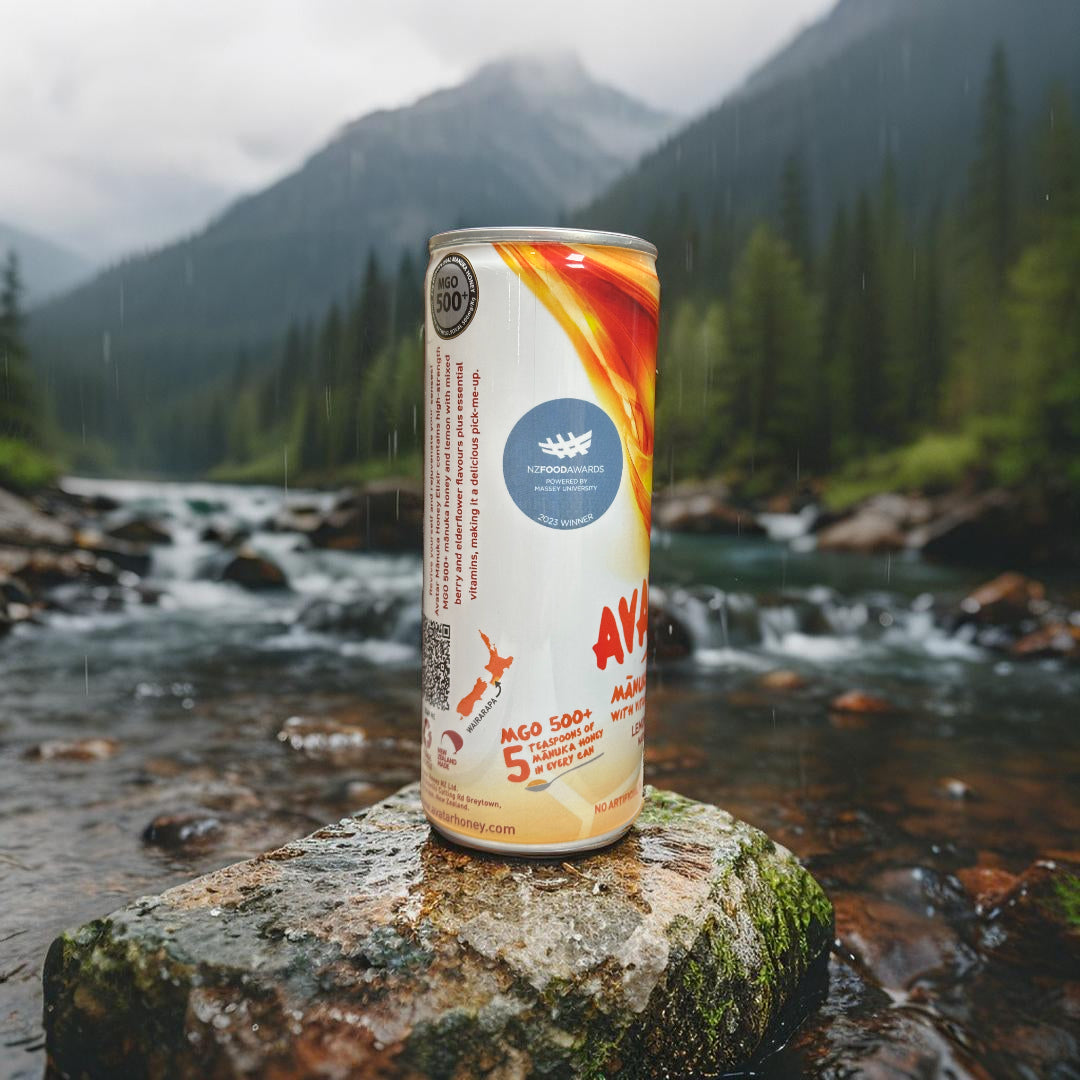
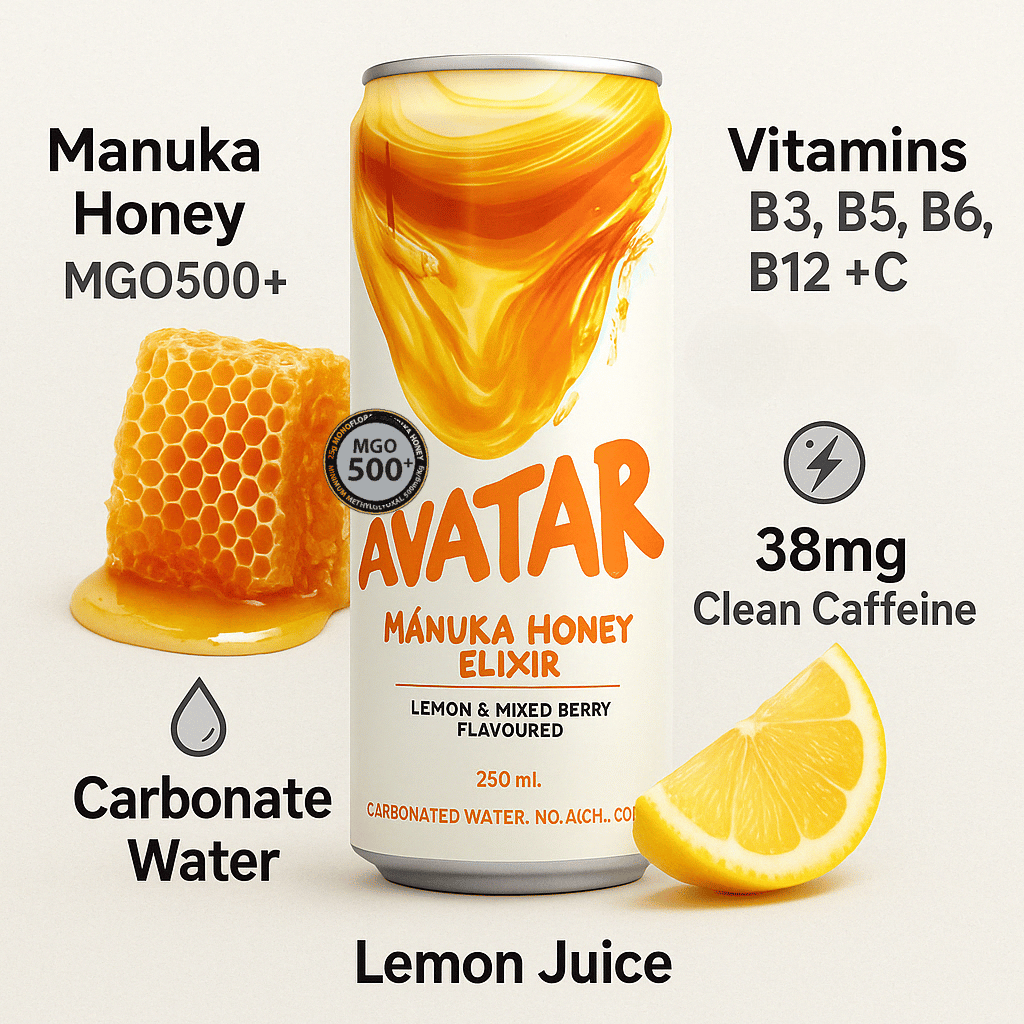
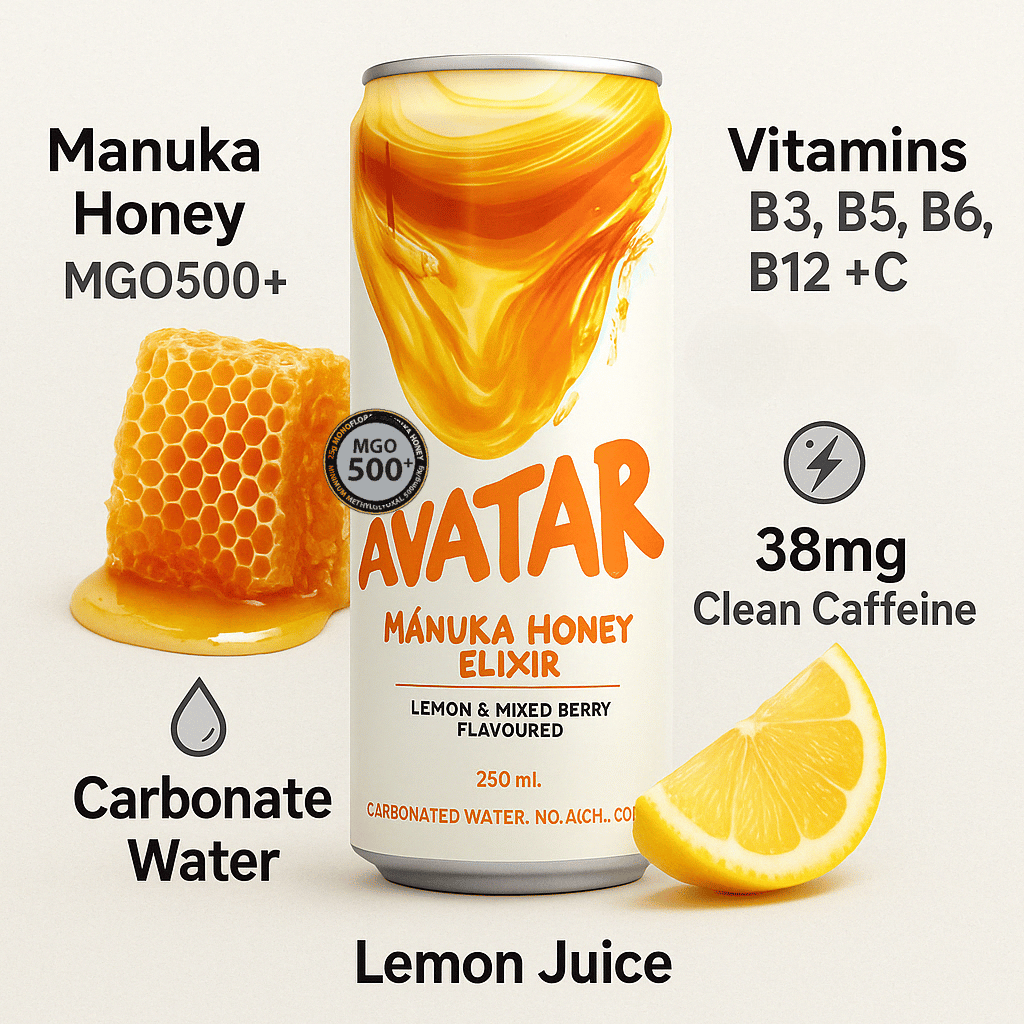
Manuka honey, in particular, contains MGO (methylglyoxal), which gives it extra antibacterial potency.
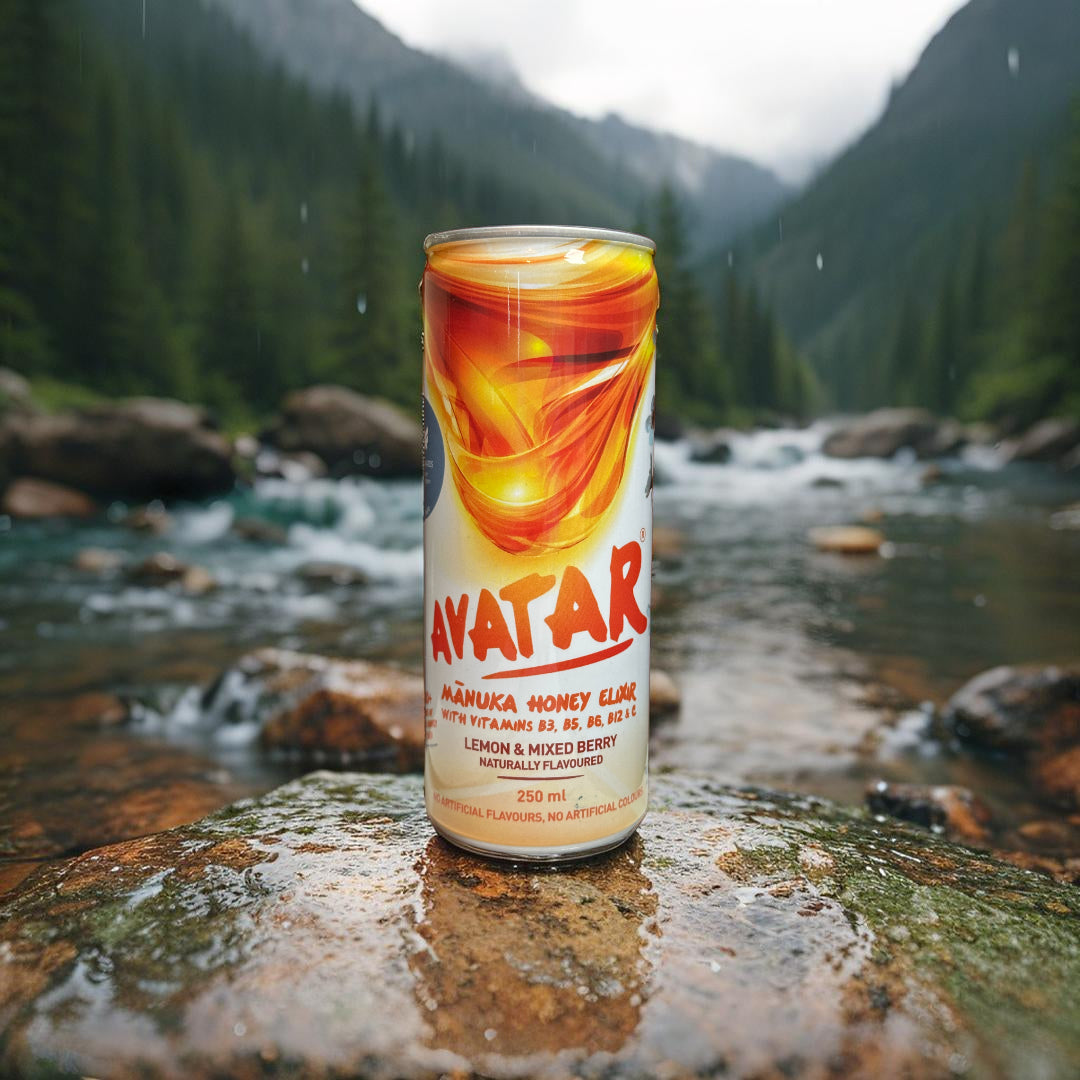
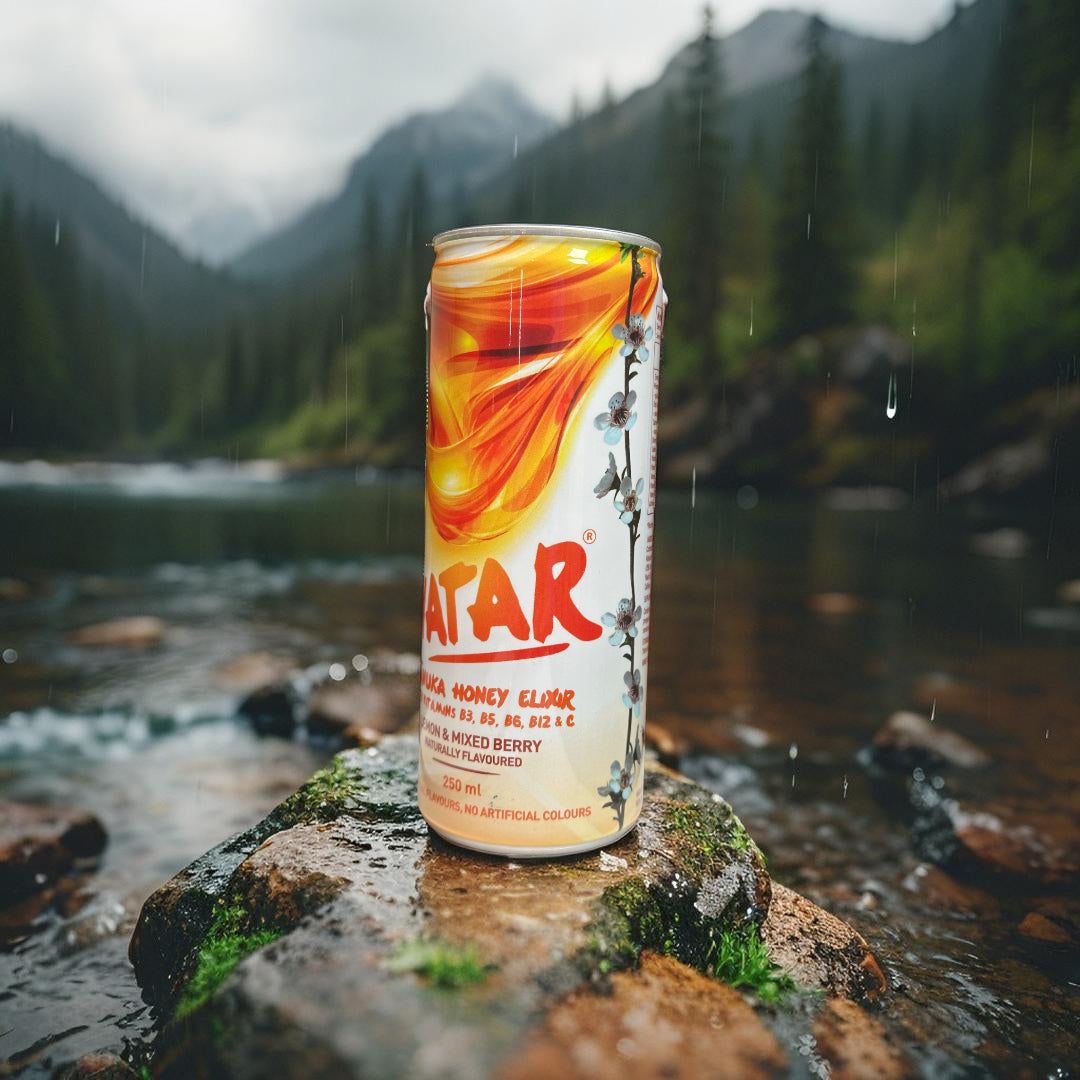
⚡ Our Approach: Real Sweetness. No Gimmicks.
When we set out to create Avatar Manuka Honey Elixir, we made a hard rule:
No artificial sweeteners. Ever.
We use real MGO500+ Manuka honey — wild-harvested in New Zealand — and let its natural sweetness do the work. We don’t hide behind sucralose or erythritol.
Each can delivers:
-
25g of real honey
-
Light carbonation
-
Natural lemon & elderflower
-
Clean energy with B vitamins
The result? A drink your body understands. A boost that doesn’t come with fine print.
🌿 Final Thoughts: Sweet Shouldn’t Be Scary
You don’t need a lab to sweeten your life.
If you’re trying to cut back on sugar without compromising your health, consider nature’s oldest energy source: honey. Especially the kind that comes from deep New Zealand forests.
Because sometimes, the healthiest move isn’t what’s new. It’s what’s always been.
👉 Want to try a clean, honey-powered energy drink?
Check out our Founder’s Offer — and taste the real difference.
Tags: artificial sweeteners, sucralose, stevia, erythritol, is honey better, zero sugar drinks, healthy energy drink, Manuka honey, clean label energy, gut-friendly drinks
Frequently Asked Questions
Is stevia an artificial sweetener?
While stevia comes from a natural plant, many commercial stevia products are highly processed and blended with artificial additives. Always check the ingredients list. For a truly natural option, raw honey is as unprocessed as it gets.
Is sucralose bad for you?
Some studies suggest sucralose may alter gut bacteria and could impact insulin response. It's commonly found in “sugar-free” drinks — but may not be as harmless as once believed.
What artificial sweetener is in Diet Coke and Coke Zero?
Diet Coke typically uses aspartame, while Coke Zero often contains a mix of aspartame and acesulfame potassium (Ace-K). Both are synthetic sweeteners under increased scrutiny in recent health studies.
Does artificial sweetener raise blood sugar?
Some sweeteners like sucralose may cause blood sugar spikes in certain individuals. Natural options like raw honey offer gentle energy without artificial spikes or crashes.
Does artificial sweetener break a fast?
Depending on your goals, some artificial sweeteners may trigger an insulin response, which could technically break a fast. Honey would break a fast too — but delivers clean energy for when your fast ends.
Is dextrose an artificial sweetener?
Dextrose is a simple sugar, usually derived from corn. It's not artificial, but it's highly processed and rapidly absorbed — leading to blood sugar spikes. Honey, on the other hand, contains natural enzymes and antioxidants.
Is stevia bad for you?
Stevia itself isn’t necessarily bad, but many stevia-based products are mixed with sugar alcohols or artificial carriers. If you're looking for a sweetener with a long history of human use, honey is the gold standard.
Does artificial sweetener cause weight gain?
Some research links artificial sweeteners to increased cravings and altered gut bacteria, which may contribute to weight gain. Choosing whole food sweeteners like honey can help support metabolic balance.
What is the healthiest sweetener?
It depends on your body and goals — but many health-conscious consumers prefer raw honey or pure maple syrup over artificial options. Manuka honey in particular has added functional health benefits.
Is allulose an artificial sweetener?
Allulose is a rare sugar found in small amounts in figs and raisins, but most commercial allulose is synthetically manufactured. While it has fewer calories, it's still relatively new and not well studied long-term.